ETFs can be used to provide low-cost1, transparent exposure to various asset classes, regions, sectors or investment styles as:
- Core investments to create the foundation of a portfolio in the process of being constructed,
- Complementary investments to help enhance the overall portfolio diversification of an existing portfolio, or
- Supplemental investments to help manage risk.
Gain access to all markets by combining ETFs and mutual funds
Combining ETFs and mutual funds within a portfolio can provide the flexibility needed to gain complete and total access to the financial markets.
Flexibility of Choice and Enhanced Diversification
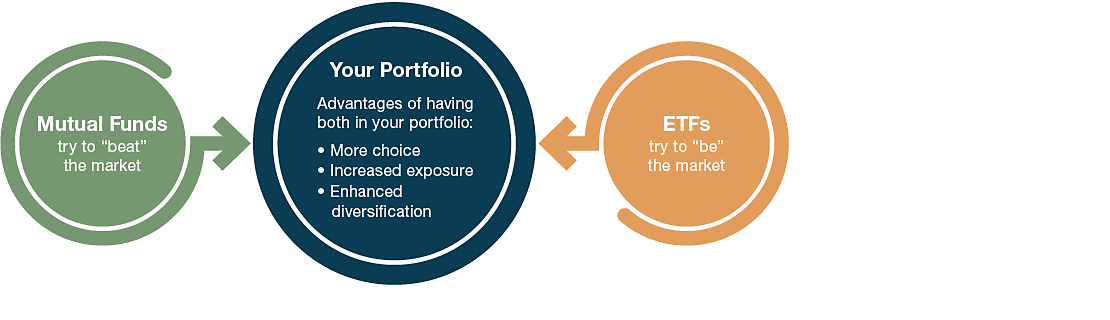
Diversification does not ensure a profit or protect against a loss in a declining market.
1. Like mutual funds, ETFs charge a management fee that is deducted directly from the assets of the fund. Therefore, the investment return of an ETF may be lower than the underlying benchmark index. This fee may be referred to in the prospectus as an “expense ratio,” management fee,” or “investor fee.” A broker’s commission fee is also assessed each time an investor purchases shares in an ETF. It’s important to note that while ETFs do not have some of the administrative costs as similar index mutual funds, they do not always have lower fees.